Plastic molding dies are a type of mold used for forming plastic products. Extrusion molding dies take the molten material from the extruder, and under the condition of being extruded, pass it through its cavity, where the structure, shape, and size of the molding meet the process requirements of the blank, which becomes a product after cooling and shaping. People often refer to this type of product mold connected to the extruder barrel as a “die head”.
Extrusion molding dies are mainly used for the production of plastic products such as pipes, sheets, and profiles. This type of mold usually consists of multiple parts, including a machine head, a shaping mold, a cooling system, etc. Extrusion molding dies are characterized by their simple structure, high production efficiency, and stable product dimensions. We will use the molding die for extruding pipes as an example to explain:
1: Principle and Characteristics of Extrusion Molding
Principle and Characteristics of Extrusion Molding
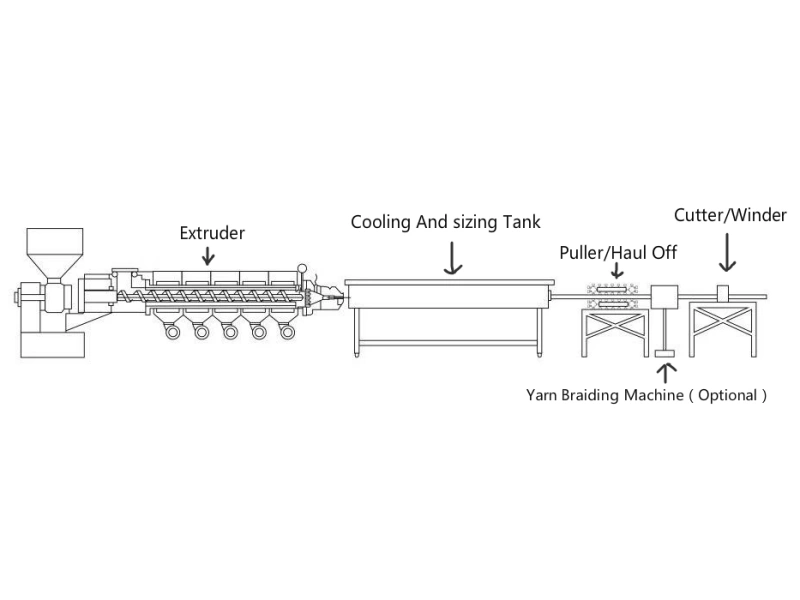
The principles and characteristics have been detailed in another article.
What Is Plastic Extrusion Line – Single Screw Type?
Extrusion Molding Process and Key Elements
- Raw Material Preparation
- Plastification Phase
- Molding Phase
- Calibration
- Traction, Curling, or Cutting of Plastic Parts
Key elements affecting extrusion molding:
- Temperature
- Pressure
- Extrusion Speed
- Traction Speed
2. Overview of Extrusion Head for Pipe Extrusion Molding:
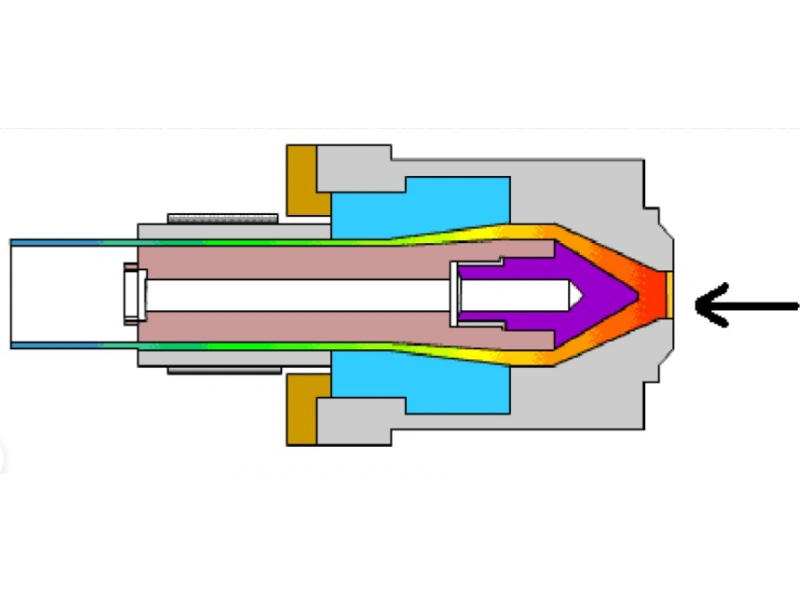
Die heads for pipe extrusion molding are commonly known as “die heads.”
Functions of Die Heads:
- Transforming plastic melt from spiral to linear motion
- Generating necessary forming pressure for dense products
- Further plasticization of the material
- Shaping the material into the required cross-sectional profile
- Classification of Die Heads:
- Based on shape: ring and flat dies
- Based on feed and discharge direction: horizontal and right-angle
- Based on purpose: film blowing heads, pipe heads, profile heads, rod heads, and sheet heads
- Design Principles:
- Streamlined internal cavity
- Adequate compression ratio to eliminate joint seams and compact material
- Correct cross-sectional shape
- Compact structure with appropriate material selection (wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant)
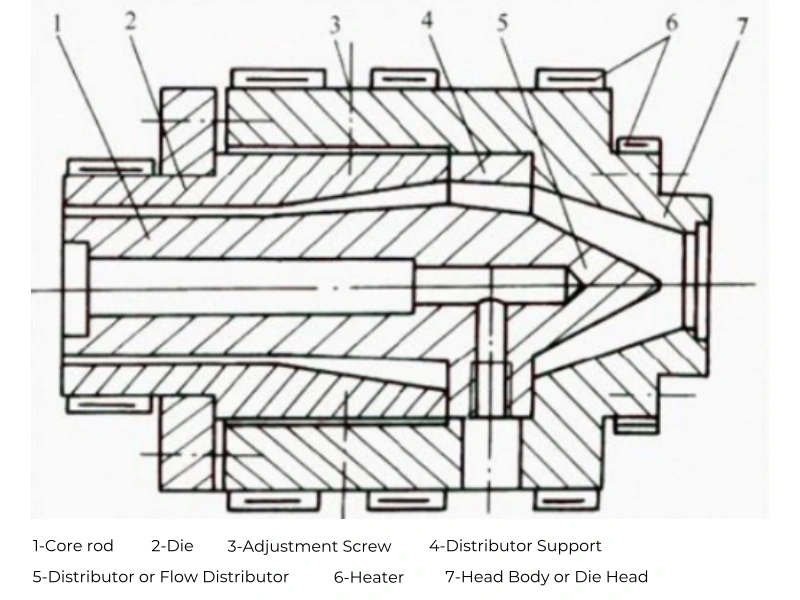
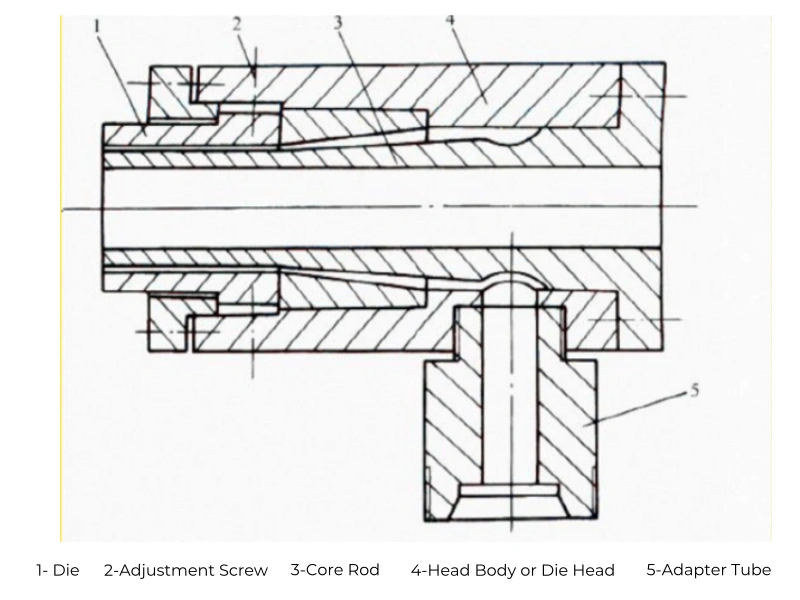
Structural Composition of the Extrusion Die Head:
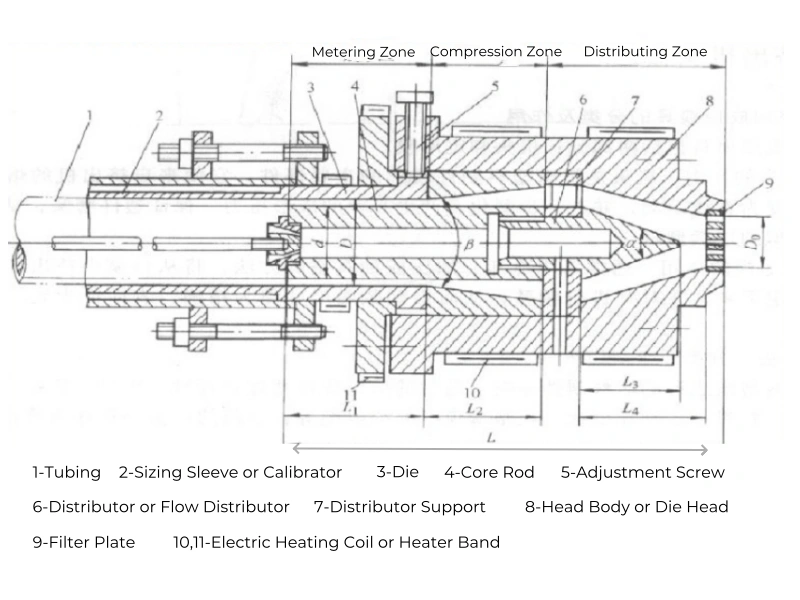
- Die:
- The die forms the outer surface of the product. The straight part of the die is the defining length, increasing flow resistance as the material passes through, ensuring product density and uniform flow.
- Sizing length L1 = (0.5~3)D, where D is the nominal size of the product’s outer diameter. Smaller values are used for larger diameters, larger values for soft pipes, and smaller values for hard pipes.
- Sizing length L1 = nt, where t is the wall thickness of the product and n is a coefficient, varying for different plastic materials (HPVC: 18~33, SPVC: 15~25, PA: 13~23, PE: 14~22, PP: 14~22).
- Inner diameter of the die, Dm, is D = k ds, where ds is the outer diameter of the plastic pipe in mm; k is the compensation coefficient, varying with different materials.
2. Core Rod:
- The core rod forms the inner surface of the product. Main dimensions include the outer diameter of the core rod, length of the compression segment, and compression angle.
- Core rod outer diameter is the die inner diameter minus twice the gap between the die and core rod, and (0.83~0.94) times the product wall thickness.
- Sizing length L2 of the core rod is equal to or slightly longer than the die length L1.
- Compression length of the core rod forms the compression zone with the corresponding conical part of the die, ensuring the elimination of flow lines before entering the sizing area.
- Core rod compression angle varies with the viscosity of the plastic (Low viscosity: 45~60degrees, High viscosity plastic: 30~50 degrees).
3. Distributor:
- The distributor bracket supports the distributor and the core rod. The distributor fins should be streamlined. Small heads use 3 fins, medium heads 4 fins, and large heads 6-8 fins.
4. Calibration Device:
- Used for external and internal diameter sizing.
- Internal pressure method for external diameter sizing involves feeding compressed air into the pipe, with a pressure of 0.02~0.10Mpa and the calibration sleeve length about three times its inner diameter.
- Vacuum method for external diameter sizing requires a vacuum level of 53~66kPa inside the calibration sleeve. The vacuum hole diameter ranges from 0.6~ 1.2mm.
- Internal diameter sizing sleeves have a taper along their length, generally between 0.6~1.0:100.
5. Draw Ratio and Compression Ratio:
- These are process parameters related to the dimensions of the die and core rod. The cross-sectional size of the die gap is determined based on the dimensions of the pipe section.
- Common draw ratios for plastic materials are: HPVC: 1.0~1,08. SPVC: 1.1~1.35. ABS: 1.0~1.10. HDPE: 1.20~1.50. LDPE: 1.10~1.20. PA: 1.30~2.00. PC: 0.90~1.05.
- The compression ratio is the ratio of the maximum feeding cross-sectional area at the junction of the die head and the multi-hole plate to the cross-sectional area of the gap between the die and core rod (Low viscosity plastics: 4~10. High viscosity plastic: 2.5~6.0).
3. Product Quality and Extrusion Molding Factor
- Product Surface Yellowing and Frequent Scorch Marks: If the extruder barrel temperature is controlled within the process range and is stable, consider:
- The distributor cone in the mold may have a large expansion angle, causing high melt flow resistance.
- There might be stagnation areas in the mold melt flow channel, hindering material flow.
- Obstructions in the flow channel.
- Continuous Longitudinal Grooves on the Product Surface: This is mainly due to blockages in the mold melt flow channel:
- There might be foreign objects lodged in part of the flow channel, or the molding area has scratches, burrs, or severe wear.
- Instability in Plastic Product Geometry and Significant Dimensional Errors: This may be caused by:
- A small compression ratio in the mold cavity.
- A short length of the mold mouthpiece sizing section.
- Deformation of the sizing sleeve or uneven mold body temperature.
Common Pipe Production Quality Issues and Mold Faults:
- Rough and Dull Product Surface
- Possible problems:
- The sizing section (straight segment) length is too short.
- High roughness value of the die’s internal surface.
- Insufficient smoothness of the cooling sizing sleeve’s internal surface.
- Low mold production temperature.
- Solutions:
- Increase the length of the straight segment.
- Reduce the roughness of the die sizing section’s internal surface.
- Polish the inner circle of the sizing sleeve to improve smoothness.
- Appropriately increase the mold’s production temperature.
- Possible problems:
- Scorch Marks or Lines on Product Surface
- Possible problems:
- High compression ratio in the mold cavity, excessive melt flow resistance, and long melt stay in the mold causing decomposition.
- High mold production temperature.
- Stagnation in the mold melt flow channel.
- Foreign objects blocking the mold cavity.
- Solutions:
- Redesign to appropriately reduce compression ratio or distributor cone angle.
- Lower the mold’s production temperature.
- Repair and smooth out the stagnation sections in the mold.
- Remove obstructions.
- Possible problems:
- Large Errors in Pipe Wall Thickness
- Possible problems:
- Uneven gap between the die and core shaft.
- Low precision in die and core shaft manufacturing, causing misalignment.
- Uneven mold temperature distribution, large temperature differences.
- Unstable melt flow from the mold mouth.
- Solutions:
- Readjust the gap between the die and core shaft.
- Inspect and remake if necessary.
- Identify and replace damaged heating elements.
- The issue is mainly due to unstable screw speed or large fluctuations in barrel process temperature; may also be affected by uneven mold temperature.
- Possible problems:
- Low Strength and Brittleness of the Pipe
- Possible problems:
- Inappropriate selection of raw materials.
- Small compression ratio.
- Insufficient length of the sizing segment.
- Solutions:
- Re-select suitable raw materials.
- Increase the compression ratio in the mold cavity; the mold may need redesigning.
- Extend the length of the sizing segment.
- Possible problems:
- Pipe Easily Bends and Deforms, Showing Water Lines
- Possible problems:
- Mainly due to unstable control of mold temperature.
- Solutions:
- Replace damaged heaters and control elements.
- Possible problems:
- Melt Lines on Pipe Surface
- Possible problems:
- Small compression ratio in the mold melt cavity.
- Solutions:
- Redesign the mold to increase the compression ratio.
- Possible problems:
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of extrusion molding tools is key to producing high-quality plastic products. By focusing on precise tool design and process control, manufacturers can overcome common challenges and achieve excellence in their extrusion operations.
Tags:
Extrusion Process (2) PA Extrusion (1) Plastic Extruders (4) Reinforced Hose (2) Success Projects (1) TPE Extrusion (1) Troubleshooting (1)

